A deeper dive into Giant's annual report.
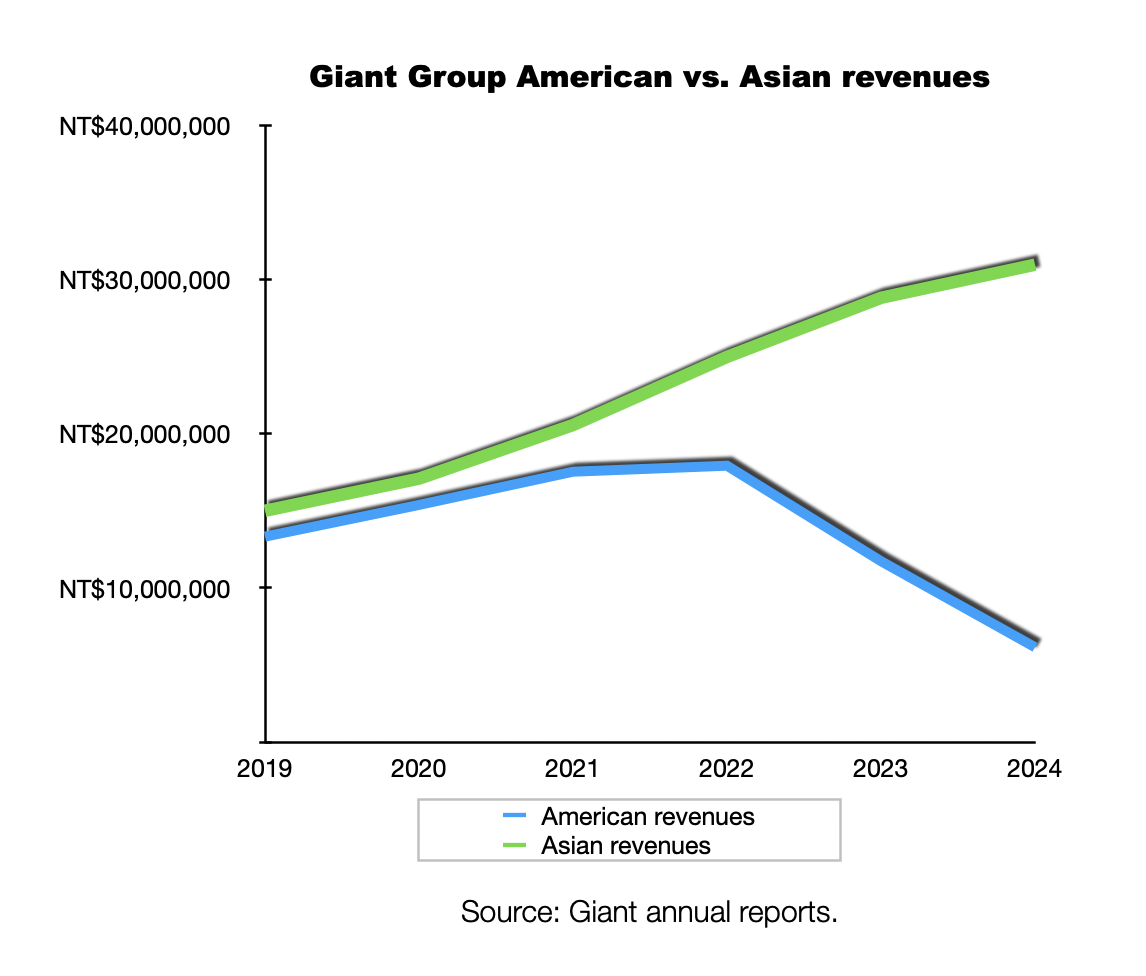
TAICHUNG, Taiwan (BRAIN) Giant Group's sales to America under its own brand and to its original equipment customers have declined steeply since the pandemic even as sales in Asia, China in particular, have grown significantly.
Giant's sales in the Americas have fallen from 21% of the the company's global revenue in 2019 to 8.6% last year, according to the company's 2024 annual report. Meanwhile, sales to Asia have grown from 24% of the global total to 44% over the same period. Giant's European sales have fluctuated within a smaller range, ranging from 37% of the total in 2019 to 34% last year.
Giantpreviously announced its 2024 annual revenues and profit figures but the annual report contains regional sales data and other information not shown in quarterly and annual financial reports, including executive and director salaries, technology and brand development overviews, manufacturing, supply and sales strategy overviews and more.
Last year Giant's operating revenues were down 7.4% from the year prior to NT$71.25 billion ($2.6 billion), down from NT$76.95 billion in 2023.Giant has noted increased sales in China specifically pointing to road bike sales there. In the annual report, Giant said sales in China remained "brilliant." While the growth is welcome in light of soft sales in the U.S., the company estimates it will pay a higher repatriation tax rate on sales in China, which tampered net profit results last year.
Regarding the regional sales mix and the change in sales in the U.S., Giant Group spokesman Ken Li said reduced sales of low-priced bikes for U.S. brands was a contributor, even as sales of higher priced Giants and higher priced bikes for other brands increased.
Asked if the company expected sales to the U.S. to reverse the trend, Li said, "Looking ahead, barring any adverse effects from U.S. trade policies on consumer sentiment, we anticipate a market recovery in terms of both volume and revenue by 2025. However, given the current uncertainty surrounding potential tariff policies under a possible Trump administration, it would be premature to make definitive projections."
Some more highlights from the annual report:
Strategy and manufacturing
Giant Group makes bikes and e-bikes in Taiwan, China, Vietnam, and Europe. In light of the Trump administration's tariff threats and anti-dumping tariffs in Europe, Giant emphasized its "transnational production base" and said it "will set short supply chain as the strategic goal to diminish the impact of trade protectionism."
"The short-term business plans include the completion of global production arrangements, the investments in automated production, and the strengthening of the short supply chain in Europe," the company said.
Inventory, interest rates and exchange rates
As noted in its fiscal reports, Giant took a NT$1.9 billion inventory impairment loss last year, but that conditions have improved, with its inventory level at the end of 2024 below 2019 levels. The company's inventory-to-asset ratio decreased from its peak of 44% to 34% by year's end. The company noted that carrying the inventory required working capital loans at high interest rates, softening profits.
Besides the reduced inventory levels going into 2025, the company noted that interest rate reductions by the U.S. Federal Reserve and expected by the European Central Bank have made it more affordable to finance inventory.
As for exchange rate fluctuations, Giant noted that a stronger U.S. dollar and Euro against the Taiwan dollar benefits is export sales to those regions, and a stronger Yen benefits sales into Japan, but works against the company when buying from Japanese suppliers. Giant said it has reached an agreement with customers to reflect exchange rate variations immediately in the quoted price if they exceed a certain range. Gant also hedges its exposure by holding "appropriate amounts" of foreign currency.
Salaries, executive changes, and board diversity
At the end of 2024, Bonnie Tu retired as board chairperson (she remains a director), Young Liu moved from CEO into the chairperson role, and Phoebe Liu was promoted to CEO.
Phoebe Liu's 2024 compensation, including salary, bonuses and pension, totaled NT$13.7 million.
Young Liu, who served as CEO throughout 2024, was compensated NT$44.5 million.
Bonnie Tu, who served as board chair through 2024, was compensated NT$55.8 million.
Giant Group's 11-member board of directors has exceeded the company's current guidelines for diversity and independence. The goal is to have at least one female director (it has four), one director with accounting experience (it has six), one with non-cycling industry experience (it has six) and three directors who are independent (it has three). Its goal for 2027 is to add one more independent director, exceeding the goal of 33% independent directors.
The independent board members include Chi-Wen Chang, the current chairperson, director, and senior advisor at Blackstone Investment; former Yahoo and Verizon executive Kai-Lien Tsou; and Chun-Sheng Ho, the co-founder of the Taiwan-based Advantech IoT company.
The board has two members who are under 50, three in their 50s, four between 61 and 70, and two older than 70.
In 2024 Giant had 10,834 employees, down from 11,415 the year before. About 32% of its employees have less than a high school education. In 2022, the Taipei Stock Exchange required listed companies to publish a diversity and equity report that included average worker salaries and education levels, which BRAIN published in our print magazine. The stock exchange has changed its requirements and the average worker salaries are no longer published.
Research and development
As the chart above shows Giant Group made a significant increase in R&D spending in 2022, in line with increased revenues that year. Since then, R&D spending has been relatively flat as revenues have softened and in 2024 the R&D spending of NT$1.42 billion (about $47 million) represented 2% of the company's revenues.